Do you often experience leg discomfort such as cramps, swelling, aches, or cold feet?
These may be signs of poor circulation. While not a disease itself, poor circulation is often linked to underlying conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol. If left untreated, it can worsen over time, raising the risk of serious complications.
What Is Poor Circulation?
Poor circulation occurs when blood flow to certain areas—often the hands and feet—becomes restricted. Since the legs are farthest from the heart, they are often the first to show symptoms.
Good circulation supplies oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing waste. When this process is disrupted, it can also affect the heart, lungs, and brain. In severe cases, blocked arteries may lead to heart attack, stroke, or even leg amputation.
Common Symptoms
Poor circulation can cause a wide range of issues, including:
• Cold feet and hands even when the body is warm
• Tingling or numbness in the extremities
• Swollen legs, varicose veins, or fluid pooling in ankles
• Muscle cramps, calf pain when walking, or joint discomfort
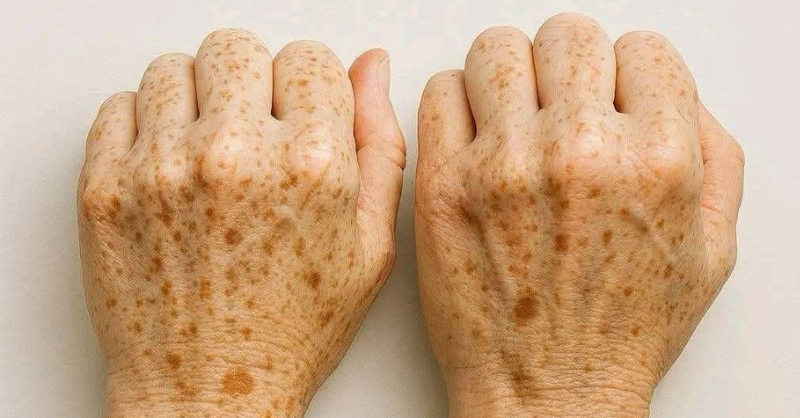
• Shiny skin, hair loss on legs, or discolored skin on fingers and toes
• Slow-healing sores or ulcers
• Dizziness, fatigue, reduced muscle strength, and memory problems
• Digestive issues such as cramps, abdominal pain, or diarrhea

Causes of Poor Circulation
Several lifestyle habits and health conditions can reduce blood flow in the legs:
1. Inflammatory diet – A diet high in sugar, refined carbs, unhealthy fats, and additives but low in fresh fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can limit nitric oxide production, raise blood sugar, and promote plaque buildup in arteries. This increases the risk of atherosclerosis, obesity, and varicose veins.
2. Sedentary lifestyle – Prolonged sitting or standing slows circulation in the legs, preventing proper oxygen and nutrient delivery.
3. Chronic stress – High stress raises blood sugar and promotes weight gain, both of which harm circulation.
4. Chronic diseases –
Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD): Fatty deposits narrow arteries, causing calf pain when walking, cold feet, and slow-healing wounds.
Diabetes & High Blood Pressure: High sugar damages blood vessels and nerves (neuropathy), causing tingling, numbness, and ulcers.
Varicose Veins & Chronic Venous Insufficiency: Faulty vein valves cause blood pooling, swelling, and heaviness in the legs.
Blood Clots & Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Poor circulation can allow clots to form, which may travel to the lungs if untreated.
Raynaud’s Phenomenon: Narrowed vessels in the fingers and toes lead to cold, numb extremities triggered by stress or cold.
5. Smoking – Tobacco use significantly raises the risk of PAD, atherosclerosis, and circulation-related disease.

How to Improve Circulation
The good news is that many habits can help restore healthy blood flow and ease discomfort.
Walk regularly – Walking strengthens calf muscles, improves blood return to the heart, and lowers stress. Aim for 30 minutes several times a week.
Adopt an anti-inflammatory diet – Colorful vegetables, fruits, nuts, whole grains, and omega-3-rich fish support vascular health while reducing plaque and inflammation.
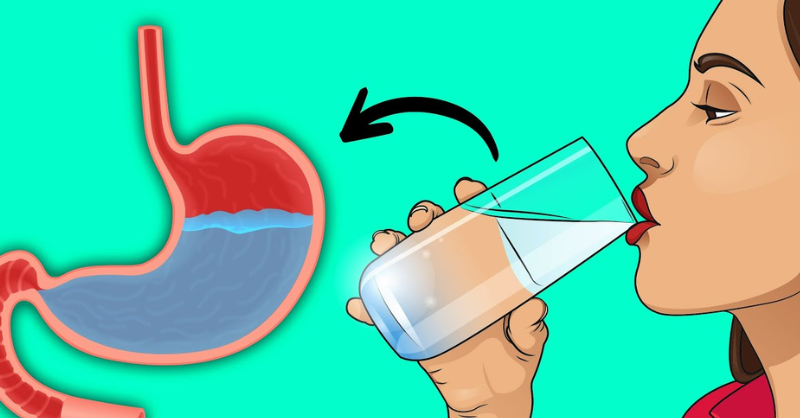
Stay hydrated – Since blood is nearly half water, hydration keeps it flowing smoothly and prevents thickening.
Wear compression socks – These provide gentle pressure to the legs, supporting veins and reducing swelling.
Elevate your legs – Raising legs above heart level for 15 minutes helps gravity move blood back to the heart.
Drink hibiscus tea – Studies show hibiscus may lower blood pressure and improve circulation thanks to its anthocyanin content.
Finally, quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake are essential steps toward protecting your circulatory health.
Takeaway
Poor circulation in the legs is often a warning sign of larger health problems. While it can cause discomfort such as swelling, cramps, and numbness, it may also indicate risks for heart attack, stroke, or vascular disease.
By making lifestyle changes—such as exercising, improving diet, and avoiding smoking—you can significantly improve circulation and safeguard long-term health.